Priapism: What It Is?
Priapism is a medical condition characterized by a prolonged, painful erection that occurs without sexual stimulation and lasts for hours longer than usual. While erections are a natural part of sexual function, priapism is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
By gaining a better understanding of priapism, you can be more aware of the signs and symptoms, and seek prompt medical attention if needed.
Also Read: Ways to Lose Mummy Tummy
Symptoms of Priapism
The most prominent symptom of priapism is an erection that lasts significantly longer than usual, typically exceeding four hours. It’s important to note that this erection occurs without any sexual stimulation or arousal.
Here’s a breakdown of some key symptoms to watch for:
- Duration: An erection lasting more than four hours is a red flag and warrants medical attention.
- Pain: Priapism, particularly ischemic priapism (low-flow), is often accompanied by pain in the penis. This pain may worsen progressively as time goes on.
- Tip of the Penis: In ischemic priapism, the shaft of the penis may be rigid and erect, while the tip (glans) remains soft.
It’s important to remember that these are just some of the common symptoms, and priapism can manifest differently in some cases. If you experience any prolonged erection, even if it’s not painful, it’s best to err on the side of caution and seek medical advice.
Causes of Priapism
Priapism can arise due to various factors that disrupt the normal blood flow within the penis. These factors can be broadly categorized into:
- Medical Conditions: Certain underlying medical conditions can contribute to priapism.
- Medications: Some medications can have priapism as a side effect.
- Other Factors: Recreational drug use and injuries can also play a role.
Let’s explore how these factors influence the two main types of priapism:
Ischemic Priapism (Low-Flow):
This is the more common type, accounting for around 30-50% of cases. In ischemic priapism, blood flow into the penis occurs normally, but there’s a problem with blood draining out. This can be caused by:
- Blood Disorders: Conditions like sickle cell disease or leukemia can alter red blood cells, causing them to obstruct blood flow within the penis.
- Pelvic Trauma: Injuries to the pelvis or genitals can damage the veins responsible for draining blood from the penis.
- Medications: Certain medications, particularly:
- Erectile Dysfunction Drugs: While meant to enhance blood flow, high doses or misuse of drugs like Viagra or Cialis can lead to priapism.
- Blood Thinners: Medications that prevent blood clotting can increase the risk of priapism, although this is uncommon.
Non-Ischemic Priapism (High-Flow):
Less frequent than ischemic priapism, this type occurs when blood flows excessively into the penis but doesn’t drain out properly. This can be caused by:
- Neurological Conditions: Conditions affecting the nervous system, such as spinal cord injuries or multiple sclerosis, can disrupt the signals controlling erection and detumescence (loss of erection).
- Recreational Drugs: Cocaine, marijuana, and certain amphetamines can cause priapism by affecting blood flow or neurotransmitters involved in erection.
- Cancers: In rare cases, tumors in the penis or pelvis can impede blood flow and lead to priapism.
Understanding the underlying cause of priapism is crucial for determining the most appropriate course of treatment.
Also Read: Must-Do Exercises for Periods
Treatment for Priapism
Priapism is a medical emergency, and seeking prompt medical attention is critical to prevent permanent tissue damage and potential erectile dysfunction. Here’s an overview of treatment options:
Emergency Interventions:
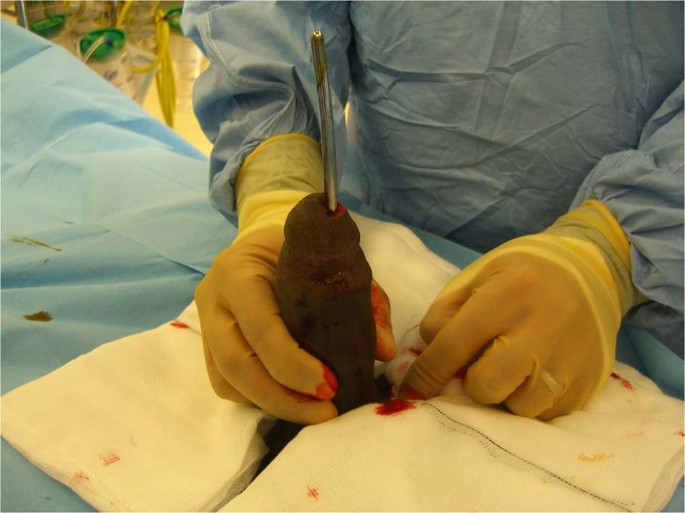
- Aspiration and Irrigation: This procedure involves using a needle and syringe to remove blood from the penis. The doctor may also flush the corpora cavernosa (erectile tissue) with saline solution to remove trapped blood cells.
- Medications: In some cases, medications like phenylephrine, a medication that constricts blood vessels, may be injected into the penis to reduce blood flow.
Longer-Term Interventions:
Surgical Procedures: If conservative measures fail, surgery might be necessary. Depending on the type of priapism, different surgical approaches can be employed, such as creating a shunt to divert blood flow or implanting materials to temporarily block blood flow.
The Importance of Early Intervention:
The longer priapism goes untreated, the greater the risk of complications. Early intervention helps to:
- Minimize tissue damage: Prolonged lack of blood flow can lead to permanent damage to the erectile tissue in the penis.
- Preserve sexual function: Early treatment can significantly improve the chances of maintaining normal erectile function.
- Identify underlying conditions: Addressing the underlying cause of priapism can prevent future occurrences.
Remember, priapism is a serious condition. If you experience an erection lasting longer than four hours, don’t hesitate to seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to a successful recovery.
How to Prevent Priapism
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent priapism entirely, certain lifestyle practices and responsible medication use can help reduce the risk:
- Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have a pre-existing medical condition known to contribute to priapism, like sickle cell disease, work closely with your doctor to manage it effectively.
- Responsible Medication Use: Only take medications as prescribed by your doctor. Be aware of potential side effects, and discuss any concerns about erectile dysfunction drugs with your healthcare provider.
- Limit Recreational Drugs: Avoid or limit the use of recreational drugs like cocaine, marijuana, and certain amphetamines, as they can increase the risk of priapism.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can contribute to overall health and potentially reduce the risk of priapism associated with certain medical conditions.
Consulting with your doctor is crucial. They can assess your individual risk factors, advise on appropriate preventative measures, and detect any underlying conditions that might contribute to priapism. Regular check-ups allow for early detection and management of potential health issues that could increase your risk.
Remember: This information is intended for general knowledge only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. If you have any concerns about priapism or experience a prolonged erection, always seek immediate medical attention.
Also Read: Foods to Help You Get Better Sleep
In Crux
Priapism, a prolonged and often painful erection, is a medical emergency requiring prompt attention. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can empower you to seek timely medical help.
If you experience a prolonged erection, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and preserve sexual health. If you have any questions or concerns about priapism, talk to your doctor. They can provide personalized advice and ensure you receive the appropriate care.
How much did you like Our detailed Priapism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment? Please share your view in the comment box. Also, please share these Blogs with your friends on social media.
Recommended